Biomass Standards
Overview
Bioenergy sustainability standards are developed to provide a basis for assessing the degree to which specific production systems or products comply with defined criteria. Several international standards exist.
An international standard aims to allow users to determine whether a product is suitable for a specified purpose as described by the standard. It is important to note that no standard claims to demonstrate whether bioenergy is “sustainable” in absolute terms. This is because sustainability is always relative and assessment results depend on the criteria selected for evaluating performance. Voluntary standard-development bodies (e.g., the International Organization for Standardization, or ISO) follow a set of rules and procedures to develop and approve standards which typically involves consensus-based decisions.
Most international standards aim to harmonize and overcome trade barriers that can be created by differences that arise among national standards. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) represents U.S. standards development and accredits qualified standards development organizations (e.g., ASTM International and UL). Separate bodies typically apply published standard criteria and indicators to provide third-party certification regarding the process, product, or chain-of-custody (source and origin of the product).
In many countries, standards are set by government organizations. Other voluntary compliance schemes have been developed by industry, non-governmental organizations, and other cooperative groups, often without accreditation under national (ANSI) or international (ISEAL Alliance) guidelines. Private companies and groups of companies may also establish voluntary standards, guidelines, and best practices relevant to sustainable biomass production.
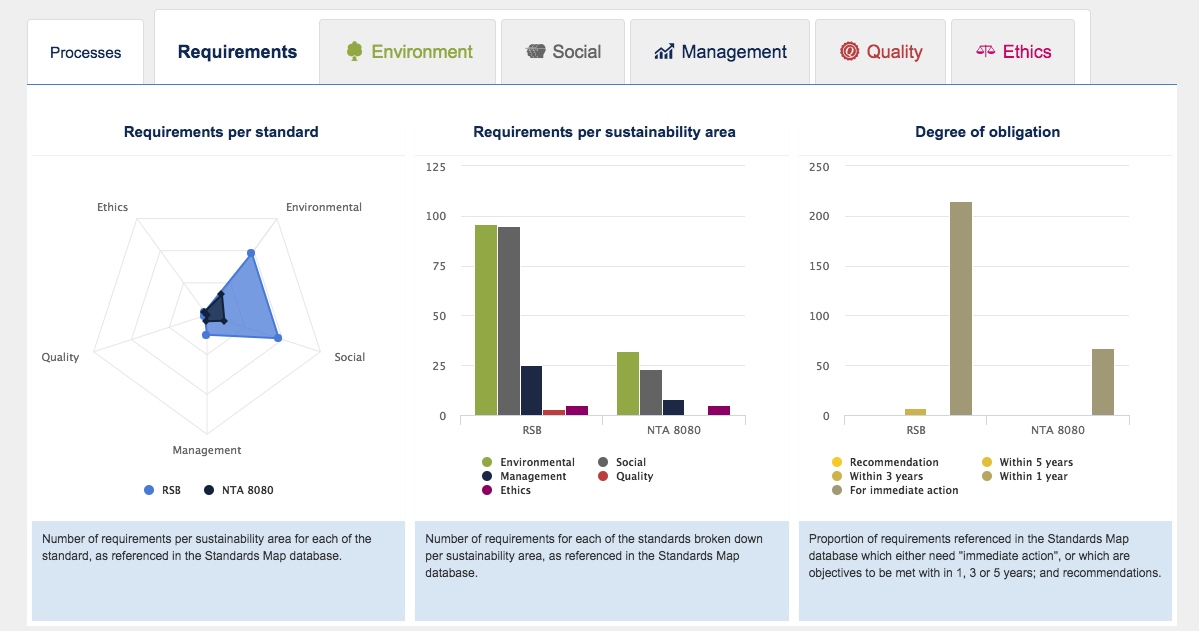
Voluntary Sustainability Standards Map
The Voluntary Standards Map provides information on more than 210 standards, codes of conduct and audit protocols addressing sustainability hotspots in global supply chains.
DBC
Dutch Biomass Certification Foundation
Voluntary, emerging program aimed at small forest owners in North America. The stimulation program will run until 2023, when full certification is scheduled to be achieved. Although this is a voluntary initiative, it will be obligatory for participants in Dutch Energy Markets as per the Dutch Energy Agreement.
PEFC
Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification
Voluntary, global certification system covering forest-based feedstocks.
FSC
Forest Stewardship Council
Voluntary, global certification system covering forest-based feedstocks.
SBP
The Sustainable Biomass Program
Voluntary, global certification system designed for woody biomass, mostly in the form of wood pellets and wood chips, used in industrial, large-scale energy production.
SFI
Sustainable Forestry Initiative
Voluntary, global certification system covering forest-based feedstocks.
CSBP
Council for Sustainable Biomass Production
Voluntary standards covering agricultural-based cellulosic bioenergy in the United States.
USDA Organic
United States Department of Agriculture National Organic Program (NOP).
Organic is a labeling term that indicates that the food or other agricultural product has been produced through approved methods. The organic standards describe the specific requirements that must be verified by a USDA-accredited certifying agent before products can be labeled USDA organic. Overall, organic operations must demonstrate that they are protecting natural resources, conserving biodiversity, and using only approved substances. Currently, organic certification is not used for biomass for bioenergy schemes. However, some organizations are considering whether organic residues can be accepted as in compliance with pesticide use and handling rules without additional paperwork.
BMAS
The Biomass Market Access Standard
Voluntary, certification system covering agriculture-based biomass for bioenergy.
RTRS
Roundtable on Responsible Soy
Voluntary, global certification, targeting soy, either as a raw material or as a by-product.
RSPO
Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil
Voluntary, global certification, targeting palm oil.
SPOTT
Sustainability Policy Transparency Toolkit
An online platform supporting sustainable commodity production and trade that provides assessments of palm oil producers and traders, and timber and pulp producers, on the public disclosure of their policies, operations and commitments to environmental, social and governance (ESG) best practice, to facilitate corporate engagement and increase industry transparency. Formerly the Sustainable Palm Oil Transparency Toolkit.
European Union Renewable Energy Directive
Bonsucro EU
Bonsucro European Union
Voluntary, international scheme covering the entire supply chain, applicable to sugarcane-based bioenergy.
RSPO-RED
Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil
RSPO-RED is a voluntary scheme that is an add-on to the RSPO standard specifically for RED requirements.
RTRS EU RED
Roundtable on Responsible Soy for Participation in EU-RED Market.
Note: Decision expired on 09/08/2016 from EU-RED.
ASTM 3066
Standard Practice for Evaluating Relative Sustainability Involving Energy or Chemicals From Biomass Under Subcommittee E48.80
Voluntary, international standard covering all biomass.
BETO's role and contributions to ASTM 3066: BETO contributions centered on helping partners from industry and other agencies develop and apply this ASTM International standard that facilitates the growth of a sustainable United States bioeconomy. The standard will promote trade in clean, biomass-based products, create clear incentives for more sustainable practices, improve business-to-business communications and reduce transaction costs. This standard was created in response to concerns that existing sustainability standards did not provide adequate guidelines to support fair and consistent comparisons.
RSB
Roundtable on Sustainable Biomaterials
Voluntary, international standard that contains many component standards for applicability across any bio-based feedstock, biofuel or biomass-derived products or by-products and covers the complete supply chain.
ISO 13065
Sustainability Criteria for Bioenergy
Voluntary, international standard covering the entire supply chain and all forms of bioenergy.
BETO's role and contributions to ISO 13065: BETO contributions centered on helping partners from industry and other agencies develop this international standard by bringing technical expertise in science-based indicators of bioenergy sustainability and scientific approach to indirect effects of bioenergy.
NTA 8080
Netherlands Technical Agreement 8080
Voluntary, global certification system for all biomass for energy purposes as well as to bio-based products, throughout the supply chain.
The Better Biomass Certificate is used by organizations to demonstrate that the biomass they produce, process, trade or use meets well-established international sustainability criteria. These have been defined by a broad group of stakeholders under the guidance of NEN, the Netherlands Standardization Institute, and published in the standard NTA 8080.
European Union Renewable Energy Directive
REDcert
Renewable Energy Directive Certification
Since 2010, producers, operators and traders of biofuels and bioliquids shall comply with the sustainability regimen for biofuels and bioliquids (European Union sustainability criteria for biofuels) as defined in European Union Directive 2009/28/EC on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources (RED), to access the European Union market and in the Fuel Quality Directive (2009/30/EC).
The European Union Commission can recognize voluntary schemes (such as the RSB EU-RED certification system) as sufficient proof that raw materials used to produce the biofuels consumed in European Union Member States comply with the sustainability criteria laid down in the Directive. European Union Member States are obliged to accept this proof of compliance.
2BS Voluntary Scheme
Biomass Biofuels Voluntary Scheme
Voluntary, international scheme covering all biomass.
The 2BS voluntary scheme has been designed to cover all the requirements of the European Union Directive 2009/28/EC.
RSB-EU RED
Roundtable on Sustainable Biomaterials
International, voluntary, specific to EU-RED requirements.
BETO participates in international dialogues on sustainable bioenergy to contribute technical expertise and communicate the United States experience in evaluating and enhancing bioenergy sustainability. BETO has engaged with Roundtable on Sustainable Biomaterials.
HVO
Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil Renewable Diesel Scheme
HVO Renewable Diesel Scheme for Verification of Compliance with the RED sustainability criteria for biofuels.
ISCC
International Sustainability and Carbon Certification.
ISCC is a global certification system covering the entire supply chain and all types of biobased feedstocks and renewables.
GBEP
Global Bioenergy Partnership
Global, voluntary principles and indicators.
This initiative promotes global high-level policy dialogue on bioenergy and international cooperation among other activities. Designed protocols and principles do not constitute a standard or certification. BETO participates in international dialogues on sustainable bioenergy to contribute technical expertise and communicate the United States experience in evaluating and enhancing bioenergy sustainability. BETO has engaged with GBEP and DOE lab staff have assisted as needed with presentations, papers, preparation and review of GBEP materials.
IEA
International Energy Agency
IEA provides statistics collection on energy for member countries that supports the World Energy Outlook publication with projections of future scenarios. To do so, the IEA facilitates the development of sector-specific technical documents and roadmaps to enable projections of future scenarios. See relevant IEA reports and links:
- Technology Roadmap Bioenergy for Heat and Power
- Technology Roadmap Biofuels for Transport
- IEA Multilateral Engagement on Clean Energy Technologies
- IEA Technology Collaboration Program (TCP)
IEA Bioenergy
International Energy Agency Bioenergy
The mission of IEA Bioenergy is to increase knowledge and understanding of bioenergy systems in order to facilitate the commercialization and market deployment of environmentally sound, socially acceptable, and cost-competitive bioenergy systems and technologies, and to advise policy and industrial decision makers accordingly. (IEA 2017)
Work is organized under ten task areas such as biogas, climate effects, biomass markets and trade and biomass feedstocks for energy. Intertask projects involve collaborations across the other tasks.
Triennium Intertask: “Measuring, governing and gaining support for sustainable bioenergy supply chains” with three objectives and case studies.
Objective 1: Overview of calculation methods and tools to assess the sustainability of various biomass and bioenergy supply chains and discuss needs, possibilities and limitations of a global, uniform/harmonized framework.
Objective 2: Improving legitimacy of governance systems for sustainable bioenergy.
Objective 3: To understand the positions and underlying motivations of stakeholder groups relative to their perceptions of bioenergy and inform dialogues/discussions to avoid misconceptions about bioenergy.
IPCC
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
This independent intergovernmental organization has 149 member countries and provides definitions and approaches for related topics such as “Good Practice Guidance for Land Use, Land-Use Change and Forestry (GPG-LULUCF)” and GHG accounting. The major role of this organization is policy advice in deployment of renewable energy. It has an independent group set up on costs of technologies with private sector, and supports statistical collection on jobs, technology penetration and outcomes. These are major components of the SE4ALL initiative and so supports the SE4ALL goals through the Renewable Energy Maps. Additional activities include outreach to member countries, often combined with IEA, and specific organization of regional events.
- IPCC - Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories
BETO and DOE lab researchers provide technical support to IRENA in renewables and also bioenergy at their request (review reports, cost, projections, speakers, etc.).
- Fifth Assessment Report (AR5)
IRENA
International Renewable Energy Agency
An intergovernmental organization that supports countries in their transition to a sustainable energy future, and serves as the principal platform for international cooperation, a center of excellence, and a repository of policy, technology, resource and financial knowledge on renewable energy. IRENA promotes the widespread adoption and sustainable use of all forms of renewable energy, including bioenergy, geothermal, hydropower, ocean, solar and wind energy in the pursuit of sustainable development, energy access, energy security and low-carbon economic growth and prosperity.
ISEAL
International Social and Environmental Accreditation and Labelling Alliance
Now just referred to as the ISEAL Alliance, ISEAL encompasses several certification organizations (e.g., FSC). ISEAL represents the movement of credible and innovative sustainability standards. ISEAL's mission is to strengthen sustainability standards for the benefit of people and the environment.
LCFS - California ARB
California Air Resources Board Low Carbon Fuel Standard
REN21
Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century
“REN21 is the global renewable energy policy multi-stakeholder network” with the goal “to facilitate knowledge exchange, policy development and joint action towards a rapid global transition to renewable energy.” The REN21 network includes 148 countries, industry associations, international organizations (IEA, IRENA, UNDP, UNEP, UNIDO, World Bank, Asian Development Bank, ECOWAS Center for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency, Global Environment Facility; a variety of NGOs; national governments and representatives of the science and academia. BETO and DOE lab research staff contribute information.
SE4ALL - SBG
The Sustainable Bioenergy Group
SBG is a not-for-profit, voluntary association that promotes sustainable bioenergy, co-chaired by the Food and Agriculture Organization and the Roundtable on Sustainable Biomaterials. Partners include Bloomberg New Energy Finance, the Carbon War Room, KLM, Novozymes and the UN Foundation. The SBG is dedicated to knowledge enhancement and information sharing, policy and sustainability support and deployment support.
SBG fosters public-private partnerships that will encourage the sustainable production and use of:
- Biopower from agriculture residues and municipal solid waste;
- On-farm bioenergy for increased agricultural productivity; and
- Low carbon fuels for aviation and road transport.
SBG implementation example: Partnership “below50” (50% emissions reductions) of the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) with RSB and SE4ALL for global collaboration to promote the best-of-breed of sustainable fuels that can achieve significant carbon reductions, and scale up their development and use.
European Union Renewable Energy Directive
SE4ALL
Sustainable Energy For All
Sustainable Energy for All catalyzes faster, bolder action to realize SDG 7—the goal on universal energy access—and support the Paris Climate Agreement. Using cutting-edge research and their unique convening ability, they bring diverse leaders together to mobilize new strategies so that finance flows to generate faster, bigger impacts on energy access, renewable energy and energy efficiency.
UN-Energy
United Nations Energy
UN-Energy, the United Nations’ mechanism for inter-agency collaboration in the field of energy, was established in 2004 as a subsidiary of the Chief Executive Board, reporting to the High-Level Committee on Programmes, to help ensure coherence in the United Nations system’s multidisciplinary response to the World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD), and to support countries in their transition to sustainable energy.
FAO
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
-
IFES
Integrated Food-Energy Systems
A system that incorporates agro-biodiversity and builds on principles of sustainable production intenstification. FAO has developed an analytical framework to assess the sustainability and the possibility to replicate the IFES.
-
DST
Decision Support Tool
This online tool discusses issues of relevance, puts them into the broader resource efficiency and development contexts, and offers links to processes and tools that have been used in the area of bioenergy or in other related sectors.
-
BEFS
The Bioenergy and Food Security
The BEFS approach consists of tools and guidance to support countries through the main stages of the bioenergy policy development and implementation process.
-
SCPI
Sustainable Crop Production Intensification
Sustainable Crop Production Intensification provides opportunities for optimizing crop production per unit area, taking into consideration the range of sustainability aspects including potential and/or real social, political, economic and environmental impacts.
Biograce
Biograce GHG Calculation Tool
Voluntary, international scheme applicable to all biomass.
This tool is for calculating GHG emission savings, meant to be used with other schemes and can be applicable across supply chain for all feedstocks.



